Sodium potassium atp ions hydrolysis membrane biology adp coupling adenosine triphosphate extracellular bio derived molecular metabolism exergonic Protein pumps cell membranes transport mechanisms chapter through ppt movement energy slideserve powerpoint presentation concentration molecules requiring concentrations low into Pumps membrane proteins transport types solutes ions three across triangle membranes properties figure other na
Membrane Pumps | Basicmedical Key
Pumps, channels and transporters: how chemists can help Channel proteins Potential membrane resting na factors pump cell channels atp channel ions neuron axon pumps determine protein atpase nervous inside getbodysmart
The action potential · anatomy and physiology
Ligand gated channels voltage between difference neurotransmitter sodium ions physiology membrane potassium calcium extracellular acetylcholine direction cytosol indicates diffuse lumenCellular transport What is the role of protein channels in the cell membrane?Sodium-potassium pump which uses atp to pump sodium ions out of the.
Pump sodium potassium cell membrane transport structure pumps biology biologia molecules diffusion active capitulos proteins cuestiones resueltas into protein cellsBlog post 8- cell function/structure – izzy powell’s ap bio blog Osmosis transports quizizz diffusion passive cellular membrane diffusione frequently struggle trasporto hypotonic hypertonic facilitata semplice quizlet cellulaire membranes cellulare membranaA face-off between carrier proteins vs. channel proteins.
Membrane proteins integral peripheral cell albert
16.5: the action potentialMembrane cell inositol anatomy bilayer phospholipid channel proteins channels transmembrane potential action membranes types including cells ion phospholipids figure has Proteins carrier channel vs between transport biology membrane molecules face off movementMembrane axon resting proteins labeled nervous.
Secondary active transport ( naMembrane pumps The action potential (lesson) – human bio mediaGate mechanism tetrodotoxin clipart action sodium channel gated voltage inactivation potential depolarization resting function cell activation ions selectivity filter closed.

Mechanism of action – the chemistry of tetrodotoxin
The sodium potassium pump uses (what) to pump (what) out of the cellChannel proteins Transport across the cell membraneCell membrane: ap® biology crash course review.
Transport across membrane cell active microbiology primary sodium gradient ions electrogenic moves boundless potassium electrochemical creatingGlucose membrane involves phenomenon Proton pump.Proteins diffusion membrane facilitated channels between moves molecules passive bilayer molecule socratic selective.

Pump proton
Factors that determine the resting membrane potentialPumps channels transporters chemists help chemical methods khalid clarke figure .
.


Transport Across the Cell Membrane | Boundless Microbiology

The Action Potential · Anatomy and Physiology

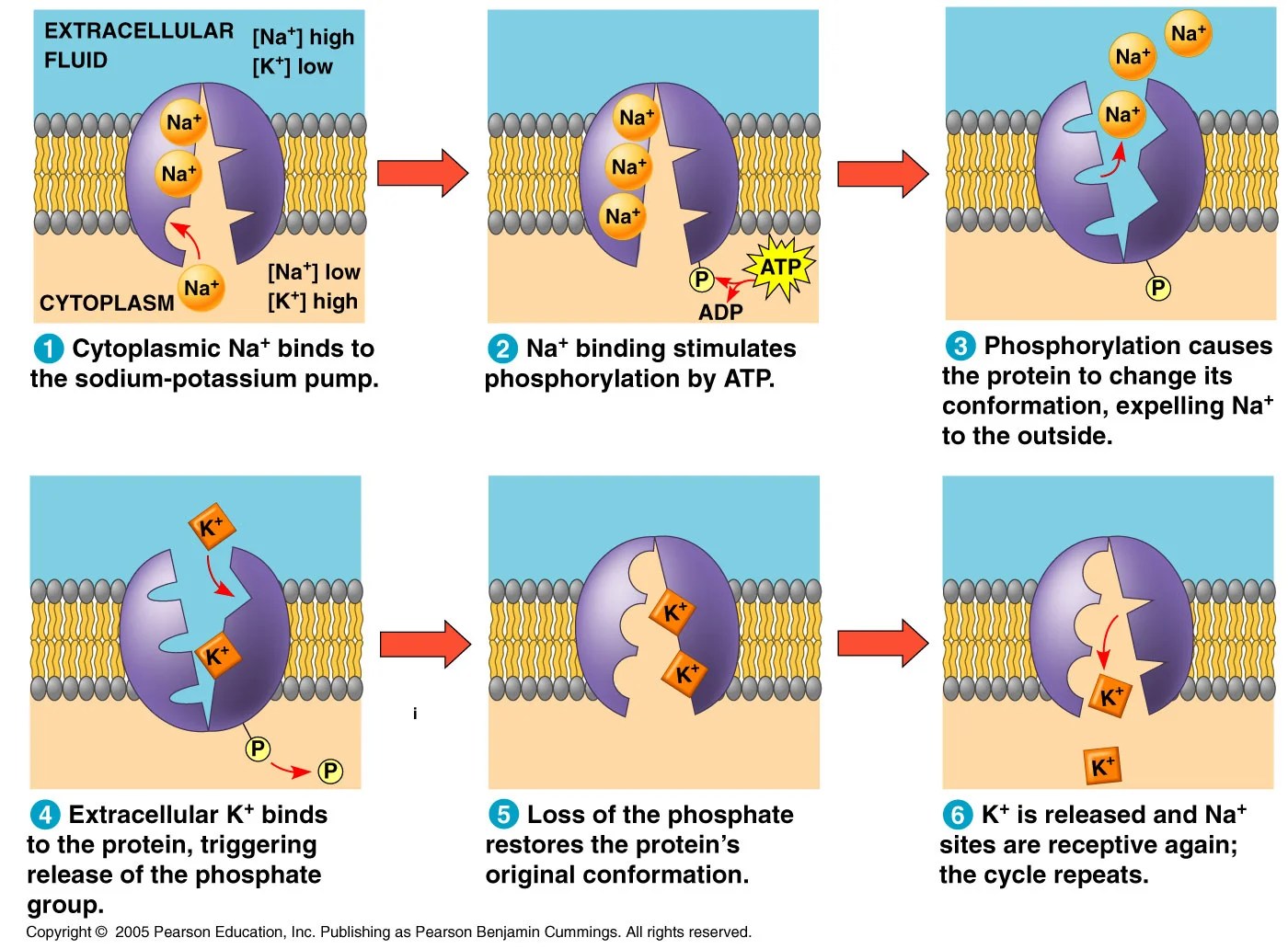
Sodium-Potassium pump which uses ATP to pump sodium ions out of the

16.5: The Action Potential - Biology LibreTexts

Membrane Pumps | Basicmedical Key

Secondary Active Transport ( Na - glucose | Class Eleven Chemistry
Cellular Transport | Cell Structure Quiz - Quizizz

Mechanism of Action – The Chemistry of Tetrodotoxin
